Introduction: Tim Berners-Lee, a name synonymous with the internet, is the visionary computer scientist who forever changed the way we communicate, share information, and connect. This detailed article delves into the life, contributions, and lasting impact of Sir Tim Berners-Lee, the architect of the World Wide Web.
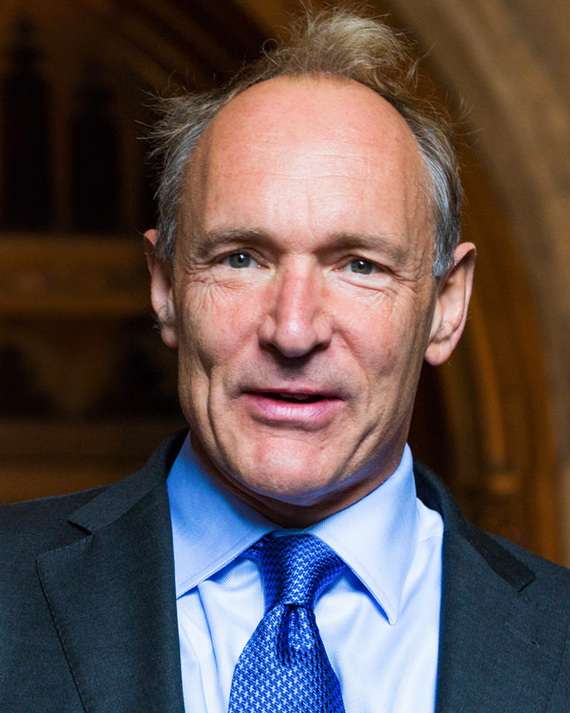

- Early Life and Education: Tim Berners-Lee was born on June 8, 1955, in London, England. His fascination with electronics and computers emerged early, and he went on to study at The Queen's College, Oxford, where he earned a degree in physics.
- Invention of the World Wide Web:
- While working at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research) in 1989, Berners-Lee conceived the idea of a decentralized information system.
- In 1990, he developed the first web browser (WorldWideWeb) and editor (WorldWideWeb.app), creating the foundation for the World Wide Web.
- The first website went live on August 6, 1991, marking the beginning of a revolutionary era.
- Key Concepts:
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Berners-Lee introduced HTTP to facilitate communication between servers and clients, laying the groundwork for web interactions.
- HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): He created HTML to structure and format documents, making content accessible and user-friendly.
- World Wide Web Consortium (W3C):
- In 1994, Berners-Lee founded the W3C at MIT, aiming to standardize and evolve web technologies.
- The consortium continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the web, maintaining web standards and protocols.
- Open Source and Collaboration:
- Berners-Lee advocated for an open and collaborative internet. He deliberately refrained from patenting the World Wide Web, ensuring its accessibility to all.
- Semantic Web:
- In the early 2000s, Berners-Lee proposed the concept of the Semantic Web, envisioning a web where data is interconnected and machine-understandable.
- This vision aims to enhance the web's capabilities in knowledge representation and reasoning.
- Knighted and Recognized:
- In 2004, Tim Berners-Lee was knighted by Queen Elizabeth II for his contributions to the development of the World Wide Web.
- He has received numerous awards, including the Turing Award and the Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering.
- Challenges and Future Concerns:
- Berners-Lee has expressed concerns about issues such as net neutrality, online privacy, and the concentration of power among tech giants.
- His work with the Solid project focuses on giving individuals control over their personal data.
- Legacy:
- Tim Berners-Lee's legacy extends far beyond the creation of the web. His commitment to openness, collaboration, and the empowerment of individuals has shaped the internet into a global phenomenon.